The hop plant is one of the most important ingredients in the brewing process, giving beer its distinctive aroma and bitterness. In this article, you will learn all about the history, cultivation, and central role of hops in brewing.
The hop plant
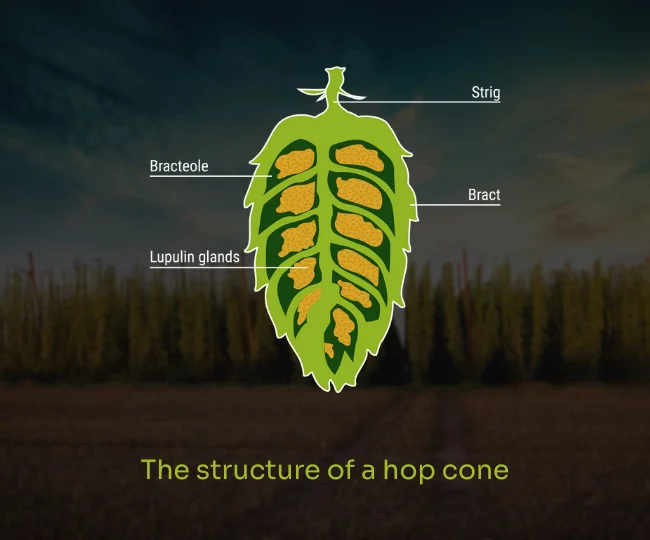
Biology of hops
Hops belong botanically to the nettle order of the hemp family. Only the female hops are required for the brewing process as these have the desired quality. The male cones / plants are not suitable for brewing beer. They are however used for breeding i.e. cultivation. As well as the bitterness and aroma in the beer, hops are also responsible for the microbiological stability. Hops also account for a good head retention and improved stability of taste. In the recent past many breweries have rediscovered long forgotten – or newly cultivated – hop varieties to help them stand out from competitors and the so-called Craft beer was born. Hop resins (alpha and beta acids) as well as hop oils and polyphenols are of utmost importance for brewers. Low rainfall or too warm a climate can adversely affect the alpha acid values. The biggest dangers for the hops are pests (common spider mites, aphids, lovage weevils, grey caterpillars,….) and fungal infections (wilt, downy mildew, powdery mildew, botrytis blight).
Cultivation & harvest
Plant, cultivate, harvest
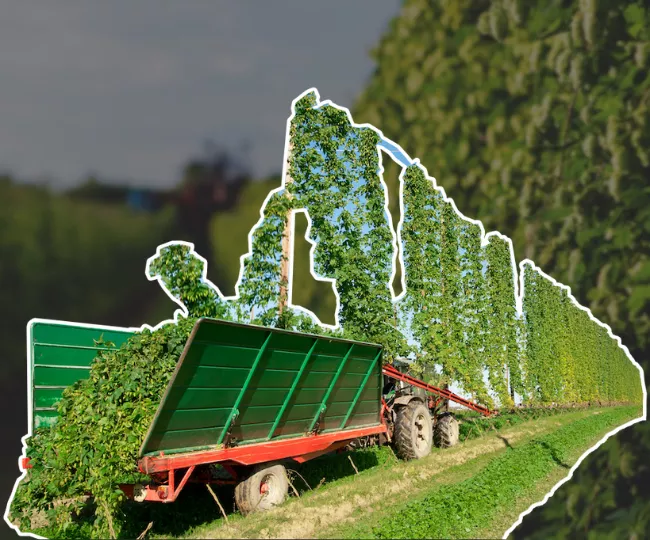
Hops are perennials, they remain in the ground for approx. 10 – 20 years and are harvested every year. This is made possible by cutting back the shoots. Using this method reduces the risk of disease and prepares the shoot for the coming harvest. Loamy or sandy soil, which is not too compact and well-drained, is ideal for the cultivation of hops. Hops require a long period of natural daylight as well as a moderate climate and therefore are grown between the 35th and 55th latitude of the northern and southern hemisphere. Hop gardens are only cleared if the yield per hectare declines, the variety is no longer in demand or if the plants are diseased. Harvest time in the northern hemisphere (USA + Europe + Japan) lies within the time frame of August to October, in the southern hemisphere (South America, Australia, New Zealand) March + April.
Growing area
Nationwide (Germany)
Hops have been grown in Germany for centuries. The cultivation of hops in the Hallertau region has only been concentrated on since the 19th century. Since the end of the Second World War the Hallertau region has emerged as the largest connected hop growing area in the world. The crop area of hops in Germany in 2020 is approx. 20.706 ha (as compared to 2019: 20.417 ha).
Worldwide
In terms of the size of the hop acreage, Germany ranks second only to the USA worldwide. Adding to this, Germany and the USA represent by far the largest and thus determining share of 71.9% of the global cultivation areas. The hop acreage worldwide in 2018 is about 60,300 ha (see 2017: 58,739 ha).
Hop categories
Aroma hops
By adding aroma hops beer is given its characteristic smooth aroma and taste.
Bittering hops
The bittering hops regulate the basic bitterness of the beer with the initial hops addition. The bittering hops do not contribute to the aroma of the beer.
Flavour hops
By adding the so-called flavour hops the beer is given a fruity fragrance and taste in a completely natural way (and conforming to the German purity law).